ARP
stands for Address Resolution Protocol. ARP acts as a layer over the
Internet Protocol address (IP) and converts it into a Media Access
Control address (MAC address) or Ethernet Hardware Address (EHA).
Understanding the concept of ARP is very important for a hacker because,
a potential hacker will be able to poison the network and steal the
information running between two servers. Hence he can execute a ‘
Man-In-The-Middle‘ attack using a simple ARP poisoning tool such as
Cain & Abel. The function of
Cain & Abel is similar to a packet sniffer.
MAC
address is a unique identification address for network nodes, such as
computers, printers, and other devices on a LAN. MAC addresses are
associated to network adapter that connects devices to networks.
The MAC address is critical to locating networked hardware devices
because it ensures that data packets go to the correct place. ARP
tables, or cache, are used to correlate network device’s IP addresses to
their MAC addresses.
How it works?
Consider
you want the phone number of a person whose name is already known to
you. In that case you will checkout your telephone book and if the
number is not available the you will call the phone service and request
him the number. Here the telephone directory act as ARP tables and the
phone service as ARP. ARP tables give the list of addresses of computers
which are connected to that system inside the network.
What is ARP poisoning?
If
a system(say System 1) requests to connect to another system(System 2)
inside the network, then System 2 checks the entry of the System 1 in
its ARP tables and if the entry is not present then it is automatically
added in System 2′s ARP tables. The weakness of the ARP is that, it
cannot identify if a person request to connect with it showing a another
address. Therefore a hacker can easily poison this network, that is, a
potential hacker if sends a request to connect to System 2 showing the
IP address of System 1 then he can access the network of System 1
associated with System 2! So he will be able to obtain the information
passing between them. That is, there is another path executed between
the System 1 and System 2.
Suppose,
if a hacker has poisoned a path between social networking site and a
victim’s system then he would be able to steal the information passing
between them, like username and password etc.
So
here, in this case the phone service is calling you and giving you the
number, even though you haven’t requested it! (Scenario mentioned above)
The concept of ARP with a simple example:
The attacker: 10.0.0.1
MAC address: 00-AA-BB-CC-DD-00
The victims: 10.0.0.2
MAC address: 00-AA-BB-CC-DD-E1
Fake address:10.0.0.3
MAC address: 00-AA-BB-CC-DD-E2
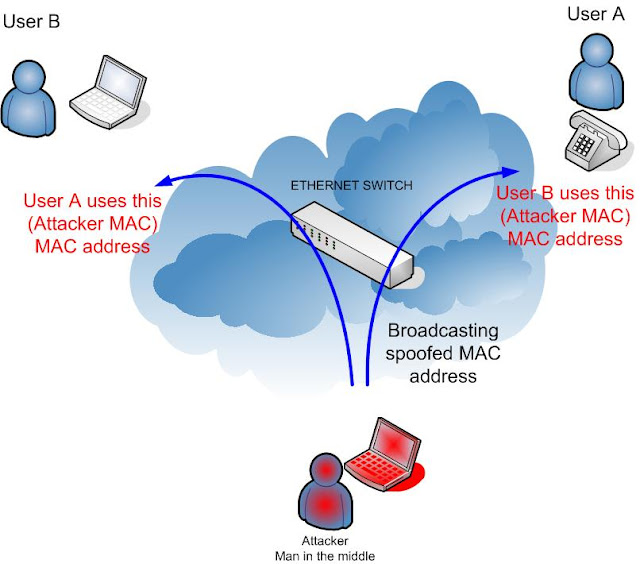
A
potential hacker sends a packet (request to connect) to 10.0.0.2 with
spoofed IP of 10.0.0.3 and then it sends a crafted package to 10.0.0.3
with spoofed IP of 10.0.0.2 with his own IP. This means that both
victims think they can find each other at the MAC address of the
attacker. This is known as Man-In-The-Middle attack
Now
all the traffic between those 2 hosts will go through the attacker
first. So this means that the attack will need to reroute the packets to
the real destination else you get a DOS on the network and there will
be no traffic possible. Also remember that the ARP tables get updated so
if during a long period of time there is no ARP poisoning the entries
will be deleted and you won’t be able to sniff until you start poisoning
again.